Urology

What is Urology?
Urology is known as a surgical specialty.
Urologist is a medical professional that specializes in the urinary system in both male and female.
Urology is branch of surgery that focuses on medical conditions of the male and female Urinary Tract - kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. It also deals with the male reproductive organs - penis, scrotum, Seminal Vesicles, Vas deferens, prostate, testes.
- Pediatric Urology (children's urology)
- Urologic Oncology (urologic cancers)
- Female Urology
- Male Infertility
- Calculi (urinary tract stones)
- Reconstructive Urology
- Neurogenic Bladder
Evaluation- for infertility is done in both male and female partners, reproductive history, sexual history, and clinical examination is done.
Diagnosis can be done by USG ovulation study, hysterosalpingography, diagnostic hystero-laparoscopy, progesterone test, endometrial biopsy, laboratory tests, urine analysis and post coital test (low validity).
Working of Kidney
You have two kidneys, located on either side of the spine just below the rib cage. Although they are small, your kidneys perform many complex and vital functions that keep the rest of the body in balance. We consume different kinds and quantities and kind of food every day.
The quantity of water, salts, and acids in our body also varies every day.
The continuous process of converting food into energy produces harmful toxic materials.
These factors lead to changes in the amount of fluid, electrolytes, and acids in the body. The accumulation of unwanted toxic materials can be life threatening.
Each kidney carries out the essential job of flushing out harmful and toxic by-products. At the same time, they also regulate and maintain the right balance and levels of water, acids, and electrolyte. For example, kidneys:
- Help remove waste and excess fluid
- Filter the blood, keeping some compounds while removing others
- Control the production of red blood cells
- Make vitamins that control growth
- Release hormones that help regulate blood pressure
- Help regulate blood pressure, red blood cells, and the amount of certain nutrients in the body, such as calcium and potassium.
Functions of Kidney
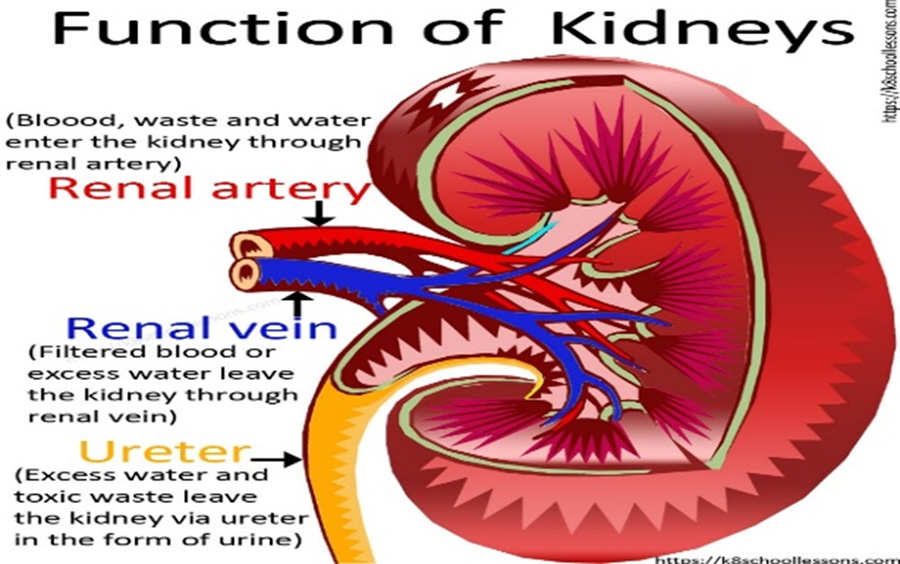
The kidneys are a very important organ in the body. They are two bean-shaped organs, located just below the rib cage, one on each side of your spine. The kidneys are responsible for getting rid of waste products, drugs, and toxins through our urine.
- Regulate electrolyte (salt) concentrations
- Regulate amount of fluid within the body
- Help regulate blood pressure
- Help maintain acid-base balance
- Produce hormones that affect blood and bones
- A kidney is composed of tiny units called nephrons
- Nephrons consist of glomeruli and tubules
- Glomeruli are small blood vessels that filter wastes and excess fluids
- Tubules collect the waste to form urine
Tips for healthy kidneys
The kidneys are important organs that affect many other body parts, including the heart,
Avoid extra salt
Eating a lot of salty foods can disrupt the balance of minerals in the blood. This can make it harder for the kidneys to work properly. Try swapping out processed foods — which usually have a lot of added salt.
Exercise
High blood pressure is a known risk factor for chronic kidney disease. Regular exercise, even for just 20 minutes a day, can help reduce blood pressure.
Stay hydrated
Drinking adequate of water helps the kidneys perform one of their most important functions: removing toxins.
Use medications with caution
Regularly taking certain over-the-counter medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, can cause kidney damage over time. Occasionally taking them is fine, but work with your doctor to find alternatives if you have a condition that requires managing pain, such as arthritis.
Know the risk factors
Several things can increase your risk of developing a kidney condition. Make sure you regularly have your kidney function tested if you:
- Have Diabetes
- are obese
- have high blood pressure
- have a family history of kidney disease
Problems that can occur in Kidney
- Urinary tract infection
- Blood in Urine - Haematuria
- Urinary incontinence
- Erectile Dysfunction
- Kidney stones
- Cystocele
- Perineal injury in males
- Pyelonephritis
- Enlargement of prostate and inflammation
- Urinary retention
- Vesicoureteral reflux
- Malignancy of urinary tract system
- Infertility
- Bed Wetting


 WhatsApp Us
WhatsApp Us